Securing communication between users and the SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) web portal is essential for protecting sensitive data and maintaining trust in reporting environments. By default, SSRS uses HTTP, which transmits data in plain text and is vulnerable to interception. To enhance security, it’s highly recommended to configure SSRS to use HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure).
HTTPS encrypts data transferred between the client and the SSRS server using SSL/TLS certificates, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity. This is especially important in enterprise environments where reports may contain sensitive financial, operational, or personal information.
This guide walks through the process of configuring HTTPS in SSRS, including:
- Prerequisites and checking the SSL certificate
- Binding the certificate to SSRS via the Reporting Services Configuration Manager
- Verifying and testing the secure connection
Environment #
- Windows
- OpeniT Analysis Server
- SSRS / Report Server Configuration Manager
Prerequisites #
- You need a valid SSL certificate installed on the server.
- This can be from a public CA (Certificate Authority), an internal CA, or self-signed.
- The certificate must have a private key and the correct hostname in the Subject or SAN.
- You must have admin rights on the server.
Checking the SSL Certificate #
Make sure the certificate is:
- Installed in the Local Computer > Personal certificate store.
- Has a private key (important!).
- Trusted by clients accessing SSRS.
How to check:
Run certlm.msc and look under: Certificates (Local Computer) > Personal > Certificates
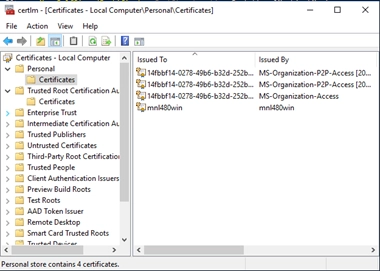
NOTE: The certificate should also be in the “Trusted Root Certification Authorities”, in case you are using a self-signed certificate as it is not trusted by default.
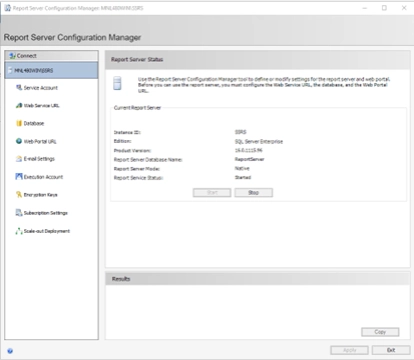
Binding the certificate to SSRS via the Reporting Services Configuration Manager #
- Open Reporting Services Configuration Manager
- Launch Reporting Services Configuration Manager
- Connect to your SSRS instance
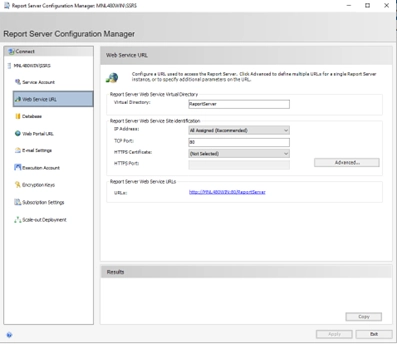
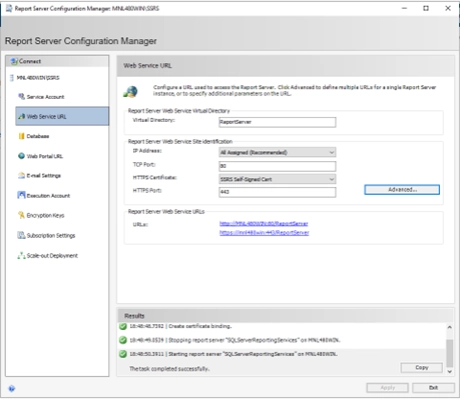
- Configure the Web Service URL (ReportServer)
- Go to the Web Service URL tab.
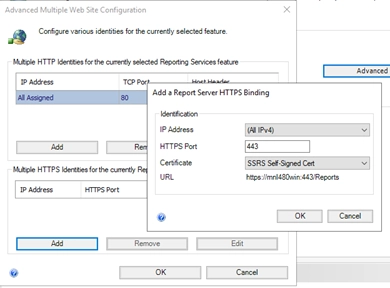
- In the HTTPS section, click Advanced…
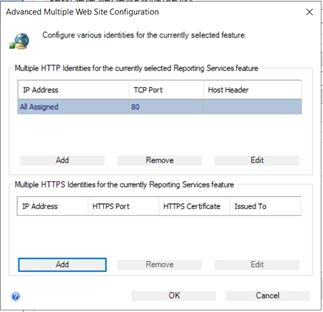
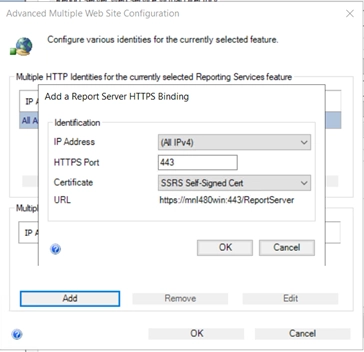
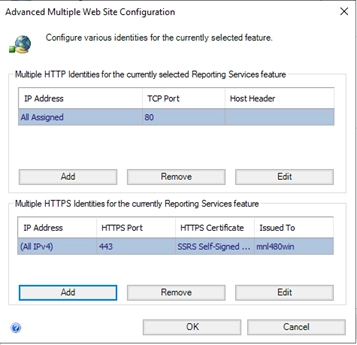
- Under Multiple SSL Identities, click Add:
- Choose the IP address (usually All Assigned)
- Select the correct SSL certificate from the dropdown
- Set the port (default is 443 or 8443)
- Click OK and Apply
- Go to the Web Service URL tab.
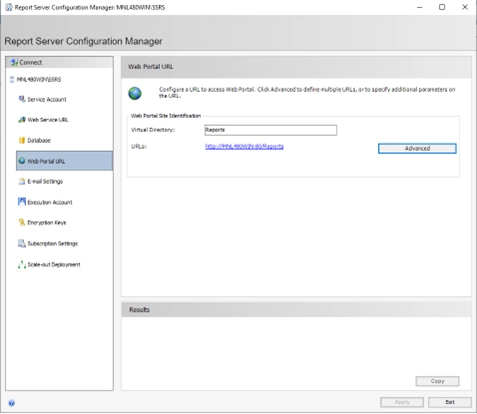
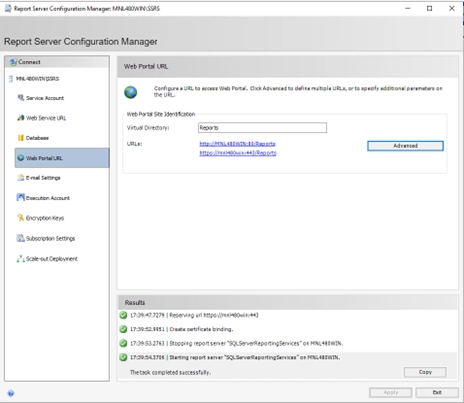
- Configure the Web Portal URL (Report Manager)
- Go to the Web Portal URL tab
- Same as above, click Advanced…
- Repeat the same steps to bind the SSL certificate
- Click OK and Apply
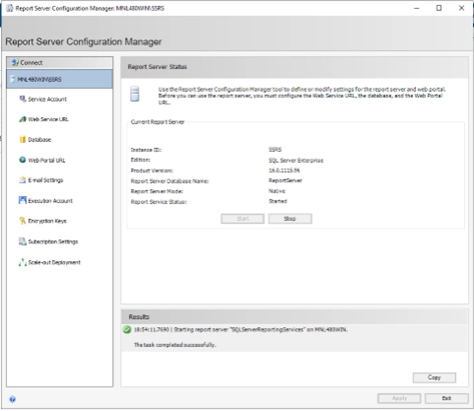
- Restart the SSRS Service
- Go to Report Server Status page and click Stop/Start or restart the SQL Server Reporting Services service from Windows Services.
- Go to Report Server Status page and click Stop/Start or restart the SQL Server Reporting Services service from Windows Services.
Verifying and testing the secure connection #
- Test HTTPS Access
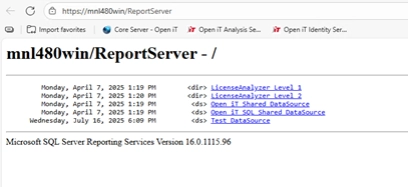
- Open a browser and go to:
- https://your-server-name/ReportServer
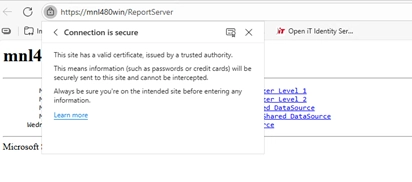
- The browser shows a secure (padlock) icon.
- https://your-server-name/Reports
- If everything is configured correctly, SSRS will load over HTTPS without any warnings.
- Troubleshooting
- If the cert doesn’t show up in the dropdown, it might:
- Be in the wrong cert store
- Be missing a private key
- Have a name mismatch
- Make sure firewall rules allow port 443 (or 8443)
- Make sure that the credential used in the Database tab of the Report Server Configuration Manager has the appropriate rights.
- Check SSRS logs (in C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSRS…\LogFiles) for errors
- If the cert doesn’t show up in the dropdown, it might:
For assistance or further configuration support, please contact your Open iT support team.
For additional references, you may visit our Documentation page.